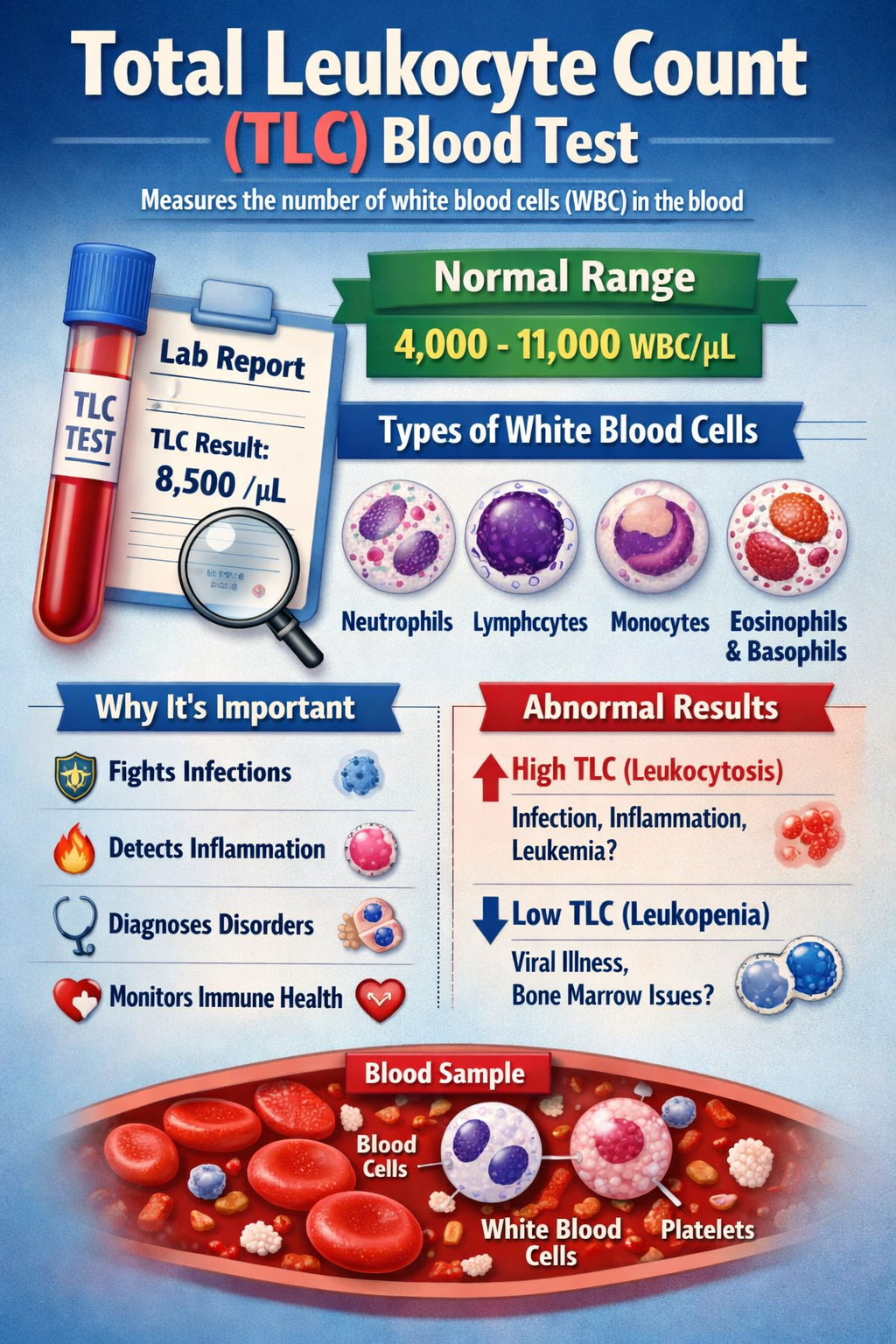
The Total Leukocyte Count (TLC) test is a key blood investigation that measures the total number of white blood cells (WBCs) in your blood. Since white blood cells are central to your immune defence, TLC provides valuable insight into infections, inflammation, immune disorders, and bone-marrow health.
What Is Total Leukocyte Count (TLC)?
Total Leukocyte Count refers to the total number of white blood cells per microlitre (µL) of blood. White blood cells include:
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Eosinophils
Basophils
Each type plays a specific role in protecting the body against infections, allergies, and inflammation.
Purpose of the TLC Blood Test
The TLC test helps to:
Assess immune system strength
Detect acute or chronic infections
Identify inflammatory and autoimmune disorders
Monitor bone marrow function
Support diagnosis of leukaemia and other blood disorders
Track response to treatments like chemotherapy or steroids
It is commonly included in a Complete Blood Count (CBC).
When Should TLC Be Tested?
Your doctor may advise a TLC test if you have:
Persistent fever, chills, or unexplained fatigue
Suspected bacterial or viral infections
Chronic inflammatory or autoimmune diseases
Allergic conditions or asthma
Unexplained weakness or weight loss
Pre-operative evaluation
Follow-up after chemotherapy, radiation, or long-term medication use
How to Prepare for a TLC Test
Preparation is simple:
No fasting is usually required
Inform your doctor about current medications
Stay well hydrated
Avoid heavy exercise just before the test
Wear clothing with easy arm access
Follow any specific instructions given by your healthcare provider.
TLC Test Procedure
A trained technician cleans the skin (usually inside the elbow)
A tourniquet is applied
Blood is drawn using a sterile needle
The sample is sent to the lab for automated analysis
Results are usually available within 24 hours
Are There Any Risks?
The TLC test is very safe. Rare minor effects include:
Mild pain or bruising at needle site
Dizziness or fainting (rare)
Infection (extremely rare)
Can Medicines Affect TLC?
Yes. Certain medications can alter WBC counts, including:
Corticosteroids
Chemotherapy drugs
Immunosuppressants
Some antibiotics
Always inform your doctor about ongoing medications.
Normal Total Leukocyte Count (TLC Range)
Adults
Normal range: 4,000 – 11,000 cells/µL
Gender variation
Males: ~5,000 – 10,000 cells/µL
Females: ~4,500 – 11,000 cells/µL
Children
Higher in infancy
Gradually decreases with age
Age-specific reference ranges are used
Interpreting TLC Results
✅ Normal TLC
Indicates a balanced immune system
🔺 High TLC (Leukocytosis)
May be seen in:
Bacterial infections
Inflammation
Stress or trauma
Allergies
Certain cancers (e.g., leukaemia)
🔻 Low TLC (Leukopenia)
May indicate:
Viral infections (e.g., hepatitis, HIV)
Autoimmune disorders
Bone marrow suppression
Vitamin deficiencies
Chemotherapy or drug toxicity
What Happens If TLC Is High?
A TLC above 11,000 cells/µL suggests leukocytosis, commonly due to infection or inflammation. Further tests (DLC, CRP, ESR) help identify the cause.
What Is Low TLC?
A TLC below 4,000 cells/µL indicates leukopenia, which may increase infection risk and requires medical evaluation.
Lifestyle Tips to Maintain Healthy TLC
Balanced diet rich in fruits & vegetables
Adequate sleep
Regular physical activity
Stress management
Good hygiene practices
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol
Conclusion
The Total Leukocyte Count (TLC) test is a simple yet powerful indicator of immune health. Whether your values are normal, high, or low, early interpretation and medical guidance can help detect infections and systemic illnesses in time. Regular monitoring and healthy lifestyle habits play a key role in maintaining optimal immune function.

Leave a Reply